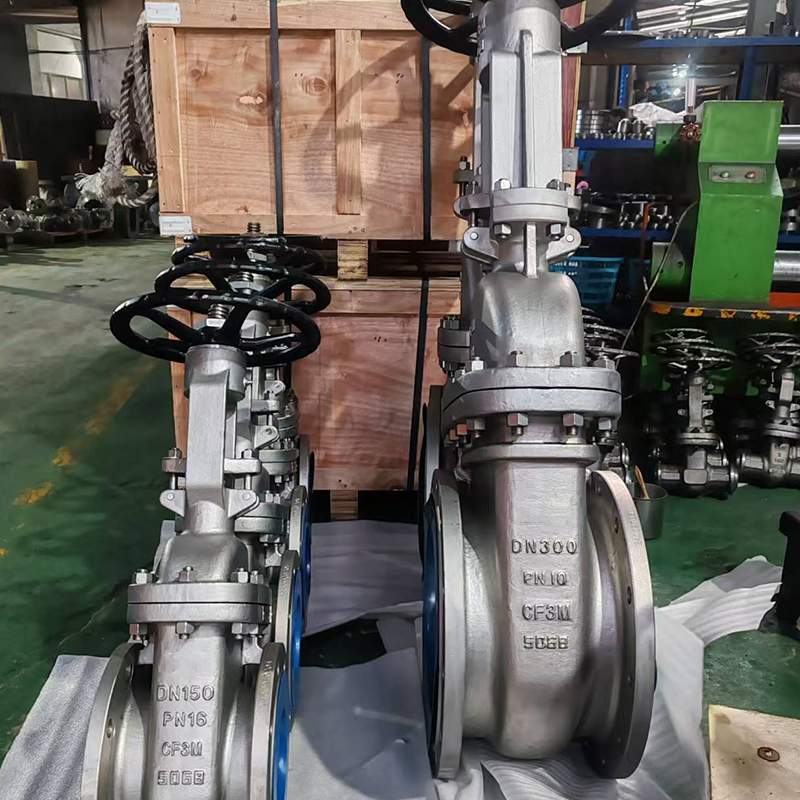

Cast steel gate valves are commonly used in various industrial applications where reliable flow control is essential. One important aspect of their performance is how they handle high pressure conditions. Understanding the capabilities and limitations of cast steel gate valves under such circumstances helps ensure safe and efficient operation in demanding environments. This article examines how cast steel gate valves perform when subjected to high pressure and what design features support their function.
Gate valves operate by lifting a gate or wedge out of the flow path to allow fluid to pass or lowering it to stop the flow. In cast steel gate valves, the body and internal components are made from cast steel, a material known for its strength and durability. Cast steel offers good resistance to pressure and mechanical stress, which is critical when valves are installed in high-pressure pipelines.
Under high pressure, cast steel gate valves must maintain a tight seal to prevent leakage. The valve’s sealing surfaces, including the gate and seats, are designed to withstand significant pressure without deforming. The precision machining of these components ensures that the gate fits closely against the seats when closed, forming a reliable barrier. Additionally, many cast steel gate valves use hardened materials or special coatings on the sealing surfaces to enhance wear resistance and maintain seal integrity under pressure.
The robust construction of cast steel bodies contributes to the valve’s ability to endure high pressure. Cast steel can handle both tensile and compressive forces, which helps prevent cracks or failures even in harsh conditions. The thick walls and reinforced design of the valve body distribute pressure evenly, reducing stress concentrations that might otherwise cause damage. This durability makes cast steel gate valves suitable for applications in oil and gas, power generation, and petrochemical industries where pressure levels can be very high.
Another factor that supports cast steel gate valve performance under high pressure is the valve’s bonnet and stem design. The bonnet is securely bolted or welded to the body to provide a strong seal and prevent leakage around the stem. The stem, which controls the movement of the gate, is often made of corrosion-resistant material and designed to operate smoothly despite the forces imposed by high pressure. Proper stem sealing, such as packing or gland seals, is also critical to maintain valve integrity and prevent leaks.
High pressure conditions can sometimes cause challenges like pressure surges or water hammer effects. Cast steel gate valves, due to their sturdy design, are generally capable of withstanding these transient conditions without failure. However, operators must ensure that valves are operated properly and that pressure fluctuations are managed to avoid undue stress.
Maintenance is important for ensuring cast steel gate valves continue to perform well under high pressure. Regular inspection of seals, seats, and stems helps identify wear or damage early. Timely repair or replacement of worn parts maintains the valve’s sealing ability and prevents operational issues.
Cast steel gate valves perform effectively under high pressure conditions due to their strong material properties, precise sealing surfaces, and robust construction. Their design supports reliable shutoff and durability in demanding environments where pressure is a significant factor. Selecting a cast steel gate valve with appropriate pressure ratings and maintaining it properly allows operators to manage high-pressure systems with confidence.

